Il existe désormais des modules Python plus simples à utiliser pour cela, comme rasterio
Rasterio utilise GDAL pour lire et écrire des fichiers en utilisant GeoTIFF et de nombreux autres formats. Son API utilise des interfaces et des idiomes Python et SciPy familiers comme les gestionnaires de contexte, les itérateurs et les ndarrays.
Par conséquent, à partir de Masquer le raster avec une entité surfacique dans Rasterio Cookbook
import rasterio
from rasterio.mask import mask
# the polygon GeoJSON geometry
geoms = [{'type': 'Polygon', 'coordinates': [[(250204.0, 141868.0), (250942.0, 141868.0), (250942.0, 141208.0), (250204.0, 141208.0), (250204.0, 141868.0)]]}]
# load the raster, mask it by the polygon and crop it
with rasterio.open("test.tif") as src:
out_image, out_transform = mask(src, geoms, crop=True)
out_meta = src.meta.copy()
# save the resulting raster
out_meta.update({"driver": "GTiff",
"height": out_image.shape[1],
"width": out_image.shape[2],
"transform": out_transform})
with rasterio.open("masked.tif", "w", **out_meta) as dest:
dest.write(out_image)
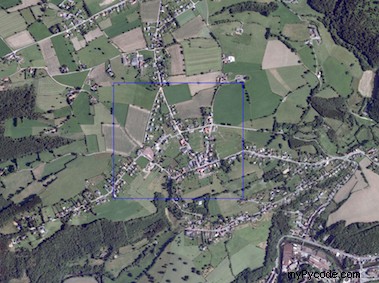
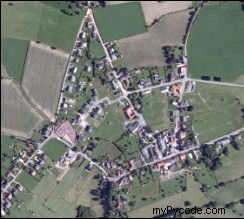
Résultat
Alternatives pour les fichiers
1) Vous pouvez simplement utiliser les modules json ou geojson pour importer la géométrie
with open('poly.json') as data_file:
geoms= json.load(data_file)
print geoms
{u'type': u'Polygon', u'coordinates': [[[250204.0, 141868.0], [250942.0, 141868.0], [250942.0, 141208.0], [250204.0, 141208.0], [250204.0, 141868.0]]]}
2) vous pouvez utiliser le module ogr avec un shapefile
from osgeo import ogr
reader = ogr.Open('poly.json')
layer = reader.GetLayer()
feature = layer.GetFeature(0)
geoms =json.loads(feature.ExportToJson())['geometry']
print geoms
{u'type': u'Polygon', u'coordinates': [[[250204.0, 141868.0], [250942.0, 141868.0], [250942.0, 141208.0], [250204.0, 141208.0], [250204.0, 141868.0]]]}
3) vous pouvez également utiliser le module Fiona
C'est un wrapper Python pour les fonctions d'accès aux données vectorielles de la bibliothèque OGR
import fiona
with fiona.open("poly.shp") as shapefile:
geoms = [feature["geometry"] for feature in shapefile]
print geoms
[{'type': 'Polygon', 'coordinates': [[(250204.0, 141868.0), (250942.0, 141868.0), (250942.0, 141208.0), (250204.0, 141208.0), (250204.0, 141868.0)]]}]
Nouveau
Vous pouvez utiliser un filtre comme dans le script de Luke dans How to set a spatial filter with Python/GDAL ?. Au lieu de couper, vous filtrez l'entrée.
from osgeo import gdal
xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax = [250204.0, 141208.0, 250942.0, 141868.0]
def map_to_pixel(mx,my,gt):
#Convert from map to pixel coordinates.
#Only works for geotransforms with no rotation.
px = int((mx - gt[0]) / gt[1]) #x pixel
py = int((my - gt[3]) / gt[5]) #y pixel
return px, py
def extent_to_offset(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,gt):
pxmin,pymin = map_to_pixel(xmin,ymin,gt)
pxmax,pymax = map_to_pixel(xmax,ymax,gt)
return pxmin,pymin,abs(pxmax-pxmin),abs(pymax-pymin)
ds=gdal.Open('test.tif')
gt = ds.GetGeoTransform()
bands = ds.RasterCount
band_list = []
#
# Read in bands and store all the data in bandList
#
for i in range(bands):
band = ds.GetRasterBand(i+1) # 1-based index
# apply filter to only read the data in the bounding box (xmin, ...)
data = band.ReadAsArray(xoff, yoff, xsize, ysize)
band_list.append(data)
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
dst_dst = driver.Create('result.tif', xsize, ysize, 4, gdal.GDT_Byte)
for j in range(bands):
data = band_list[j]
dst_dst.GetRasterBand(j+1).WriteArray(data)
....
dst_dst = None
Il vous suffit d'ajouter le crs
Voici ma propre solution. Cela fonctionne pour n'importe quel nombre de bandes, n'importe quel type de géométrie (par exemple multipolygone) et fonctionne avec des images n'importe quelles zones !
import geojson as gj
from osgeo import ogr, osr, gdal
# Enable GDAL/OGR exceptions
gdal.UseExceptions()
# GDAL & OGR memory drivers
GDAL_MEMORY_DRIVER = gdal.GetDriverByName('MEM')
OGR_MEMORY_DRIVER = ogr.GetDriverByName('Memory')
def cut_by_geojson(input_file, output_file, shape_geojson):
# Get coords for bounding box
x, y = zip(*gj.utils.coords(gj.loads(shape_geojson)))
min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y = min(x), max(x), min(y), max(y)
# Open original data as read only
dataset = gdal.Open(input_file, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
bands = dataset.RasterCount
# Getting georeference info
transform = dataset.GetGeoTransform()
projection = dataset.GetProjection()
xOrigin = transform[0]
yOrigin = transform[3]
pixelWidth = transform[1]
pixelHeight = -transform[5]
# Getting spatial reference of input raster
srs = osr.SpatialReference()
srs.ImportFromWkt(projection)
# WGS84 projection reference
OSR_WGS84_REF = osr.SpatialReference()
OSR_WGS84_REF.ImportFromEPSG(4326)
# OSR transformation
wgs84_to_image_trasformation = osr.CoordinateTransformation(OSR_WGS84_REF,
srs)
XYmin = wgs84_to_image_trasformation.TransformPoint(min_x, max_y)
XYmax = wgs84_to_image_trasformation.TransformPoint(max_x, min_y)
# Computing Point1(i1,j1), Point2(i2,j2)
i1 = int((XYmin[0] - xOrigin) / pixelWidth)
j1 = int((yOrigin - XYmin[1]) / pixelHeight)
i2 = int((XYmax[0] - xOrigin) / pixelWidth)
j2 = int((yOrigin - XYmax[1]) / pixelHeight)
new_cols = i2 - i1 + 1
new_rows = j2 - j1 + 1
# New upper-left X,Y values
new_x = xOrigin + i1 * pixelWidth
new_y = yOrigin - j1 * pixelHeight
new_transform = (new_x, transform[1], transform[2], new_y, transform[4],
transform[5])
wkt_geom = ogr.CreateGeometryFromJson(str(shape_geojson))
wkt_geom.Transform(wgs84_to_image_trasformation)
target_ds = GDAL_MEMORY_DRIVER.Create('', new_cols, new_rows, 1,
gdal.GDT_Byte)
target_ds.SetGeoTransform(new_transform)
target_ds.SetProjection(projection)
# Create a memory layer to rasterize from.
ogr_dataset = OGR_MEMORY_DRIVER.CreateDataSource('shapemask')
ogr_layer = ogr_dataset.CreateLayer('shapemask', srs=srs)
ogr_feature = ogr.Feature(ogr_layer.GetLayerDefn())
ogr_feature.SetGeometryDirectly(ogr.Geometry(wkt=wkt_geom.ExportToWkt()))
ogr_layer.CreateFeature(ogr_feature)
gdal.RasterizeLayer(target_ds, [1], ogr_layer, burn_values=[1],
options=["ALL_TOUCHED=TRUE"])
# Create output file
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName('GTiff')
outds = driver.Create(output_file, new_cols, new_rows, bands,
gdal.GDT_Float32)
# Read in bands and store all the data in bandList
mask_array = target_ds.GetRasterBand(1).ReadAsArray()
band_list = []
for i in range(bands):
band_list.append(dataset.GetRasterBand(i + 1).ReadAsArray(i1, j1,
new_cols, new_rows))
for j in range(bands):
data = np.where(mask_array == 1, band_list[j], mask_array)
outds.GetRasterBand(j + 1).SetNoDataValue(0)
outds.GetRasterBand(j + 1).WriteArray(data)
outds.SetProjection(projection)
outds.SetGeoTransform(new_transform)
target_ds = None
dataset = None
outds = None
ogr_dataset = None