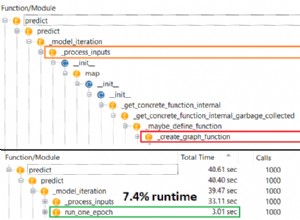
A la fin du GradientTape boucle, conv_output et grads détient déjà la valeur. La fonction itérer n'a plus besoin de calculer les valeurs.
Exemple de travail ci-dessous :
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras import preprocessing
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras import models
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
image_size = 224
# Load pre-trained Keras model and the image to classify
model = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16()
image = np.random.random((image_size, image_size, 3))
img_tensor = preprocessing.image.img_to_array(image)
img_tensor = np.expand_dims(img_tensor, axis=0)
img_tensor = preprocess_input(img_tensor)
conv_layer = model.get_layer("block5_conv3")
heatmap_model = models.Model([model.inputs], [conv_layer.output, model.output])
# Get gradient of the winner class w.r.t. the output of the (last) conv. layer
with tf.GradientTape() as gtape:
conv_output, predictions = heatmap_model(img_tensor)
loss = predictions[:, np.argmax(predictions[0])]
grads = gtape.gradient(loss, conv_output)
pooled_grads = K.mean(grads, axis=(0, 1, 2))
heatmap = tf.reduce_mean(tf.multiply(pooled_grads, conv_output), axis=-1)
heatmap = np.maximum(heatmap, 0)
max_heat = np.max(heatmap)
if max_heat == 0:
max_heat = 1e-10
heatmap /= max_heat
print(heatmap.shape)